Click image to enlarge with full caption. Main text below slider.
Rostanga rubra (Risso, 1818)
PDF available at www.researchgate.net/publication/359974136_Rostanga_rubra…
Current taxonomy: World Register of Marine Species
www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=141404
Synonyms: Doris rubra Risso, 1818; Doris coccinea Forbes, 1848; Rostanga rufescens Iredale & O’Donoghue, 1923; Rostanga temarana Pruvot-Fol, 1953.
GLOSSARY BELOW
Description
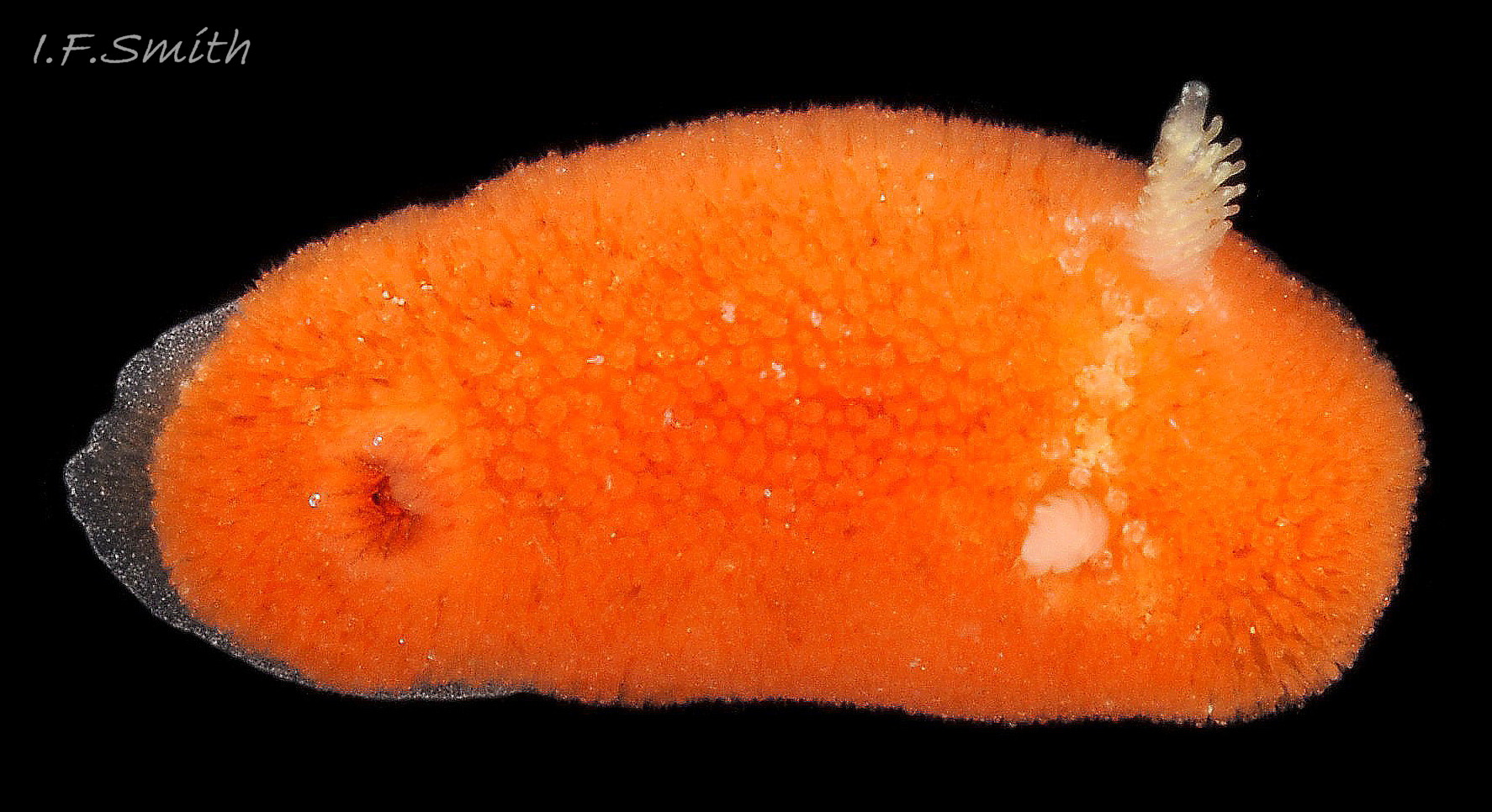
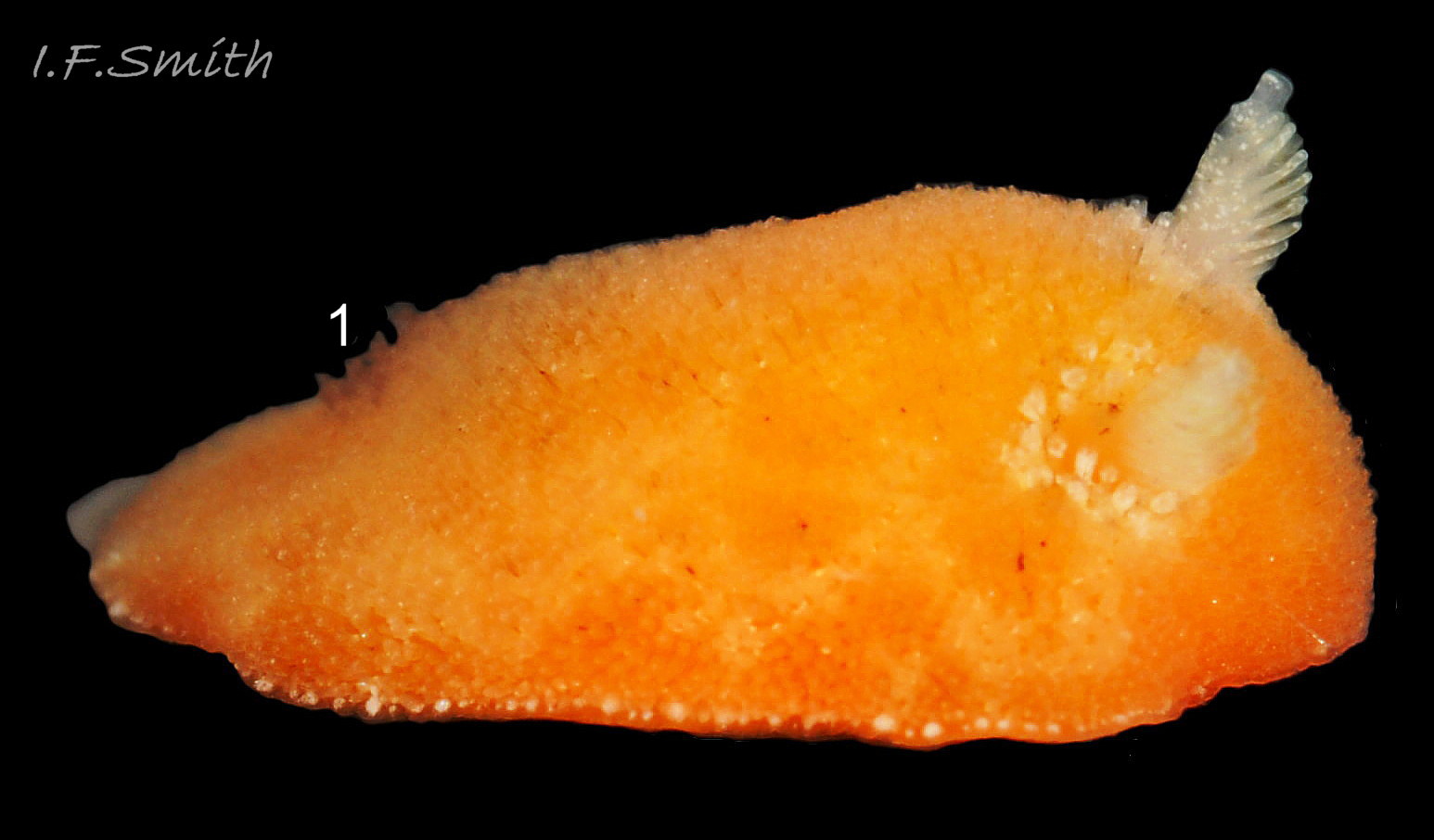
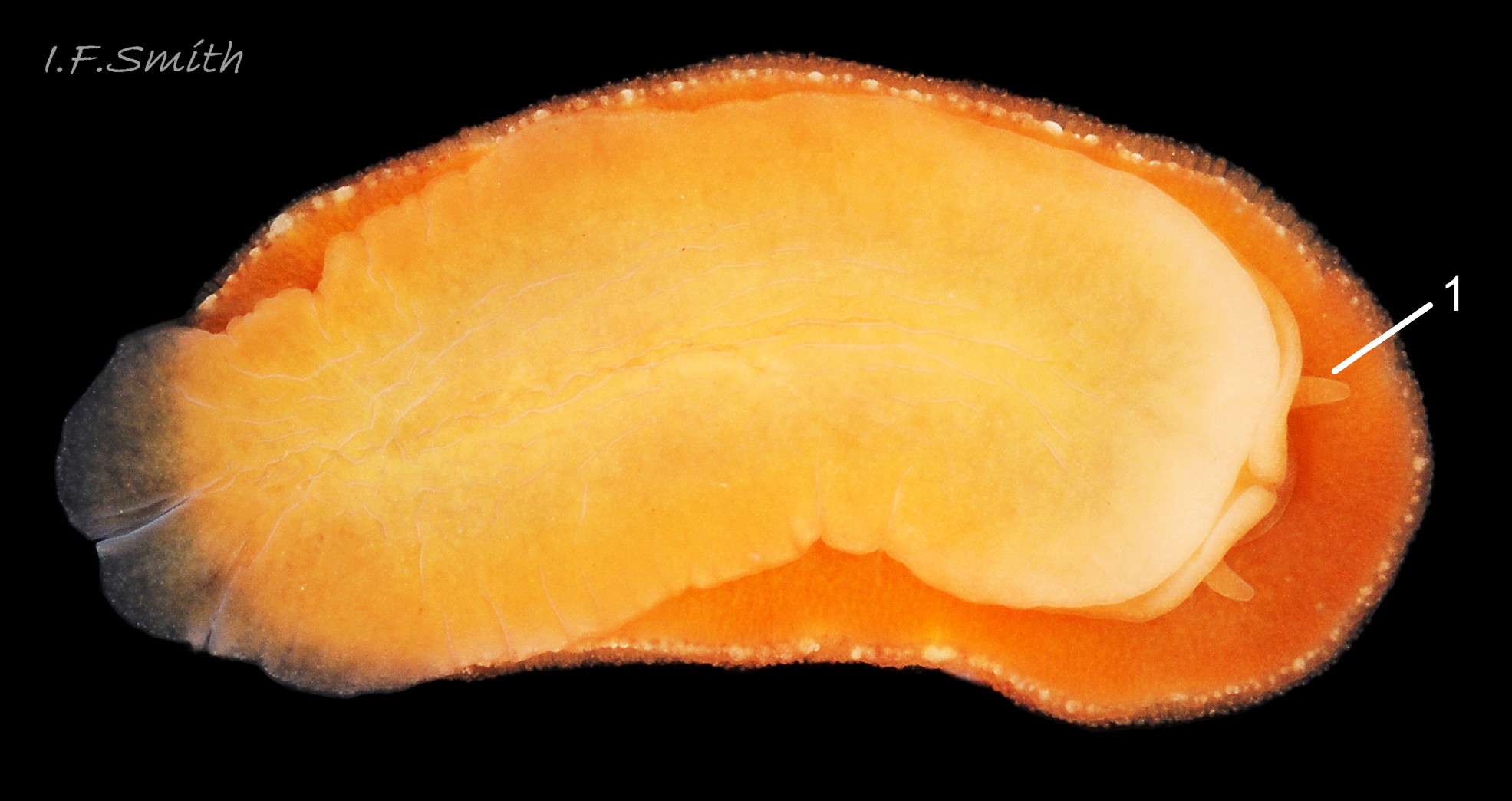
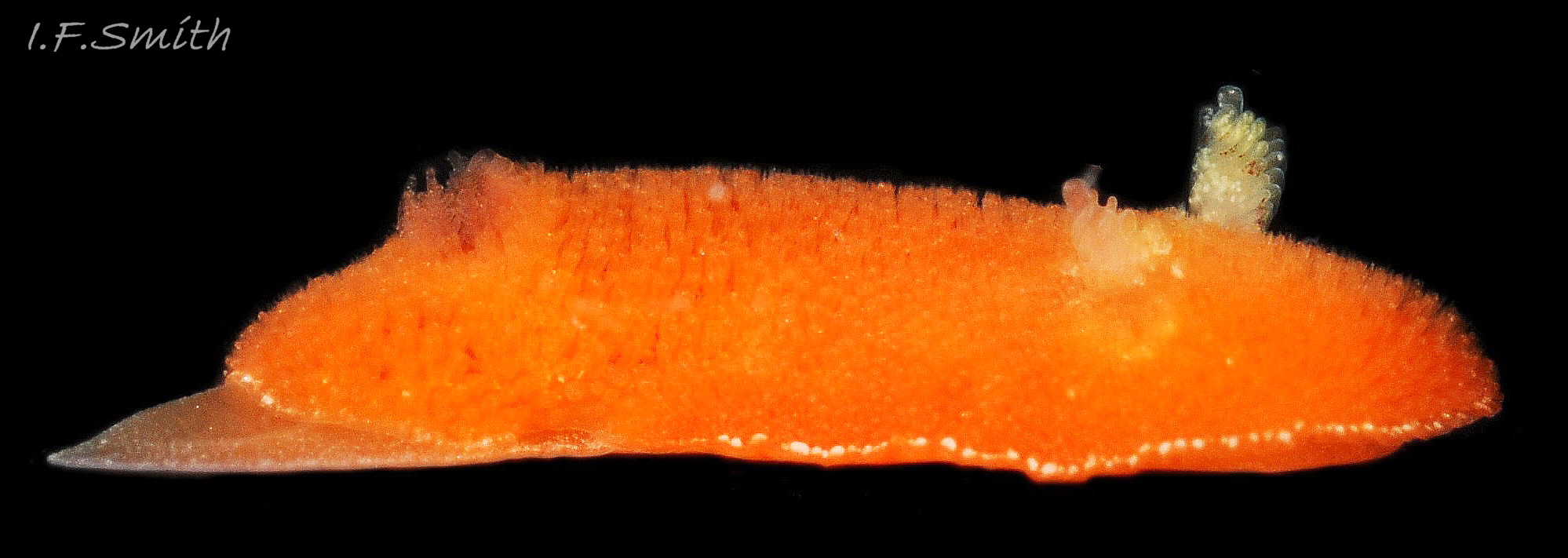
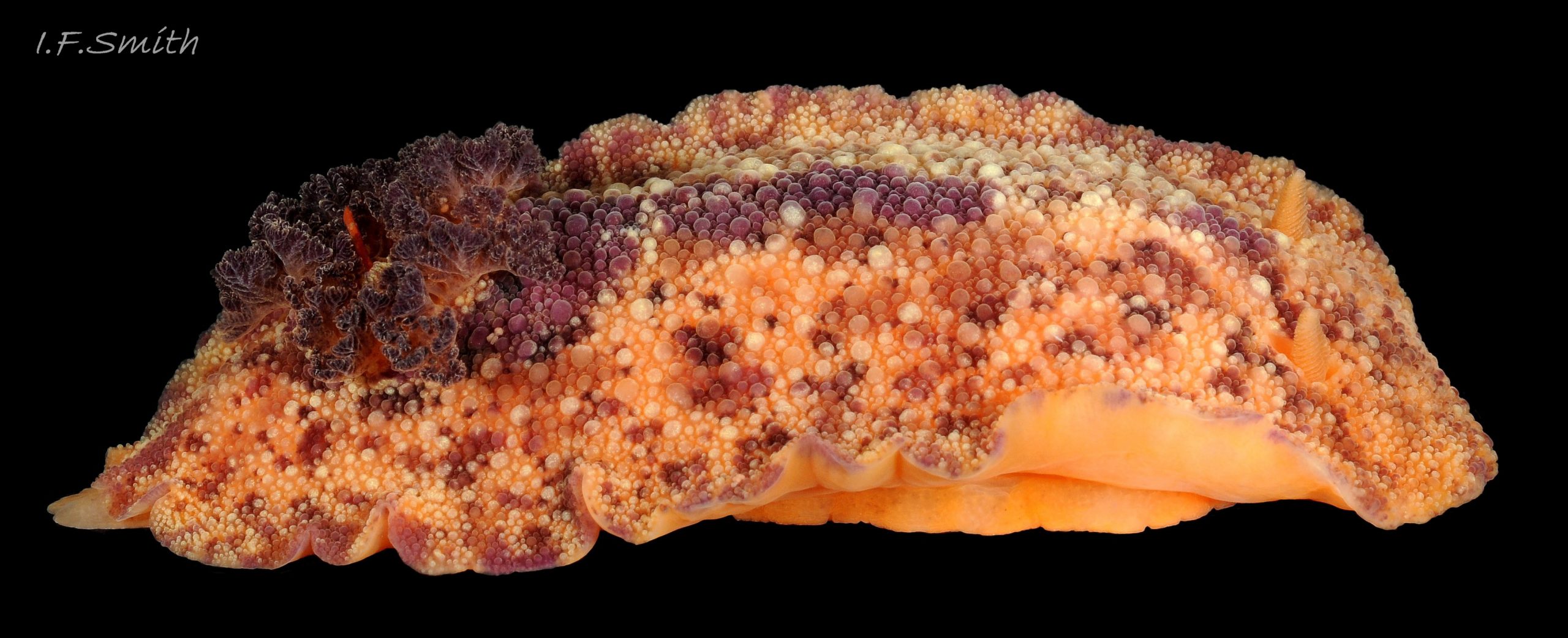
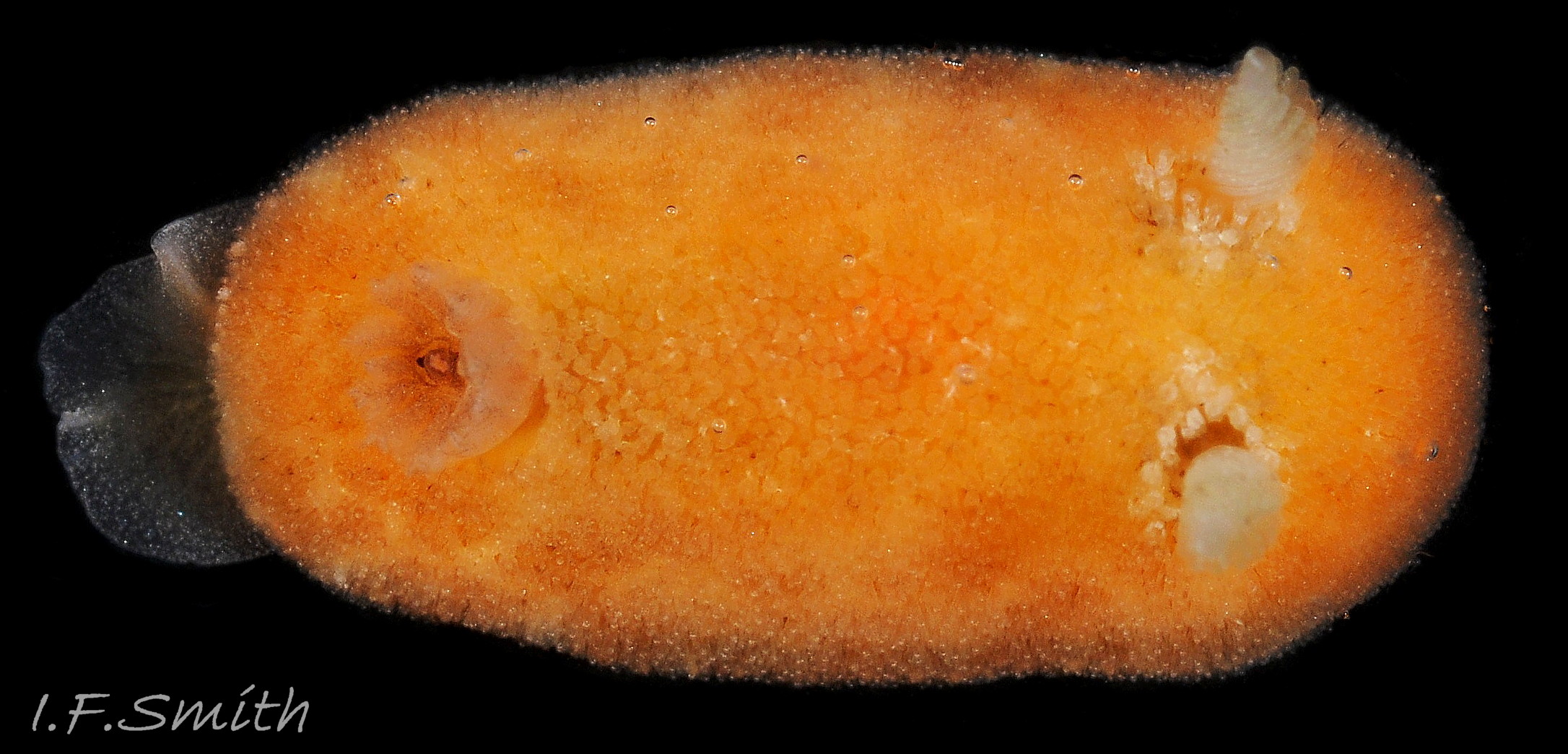
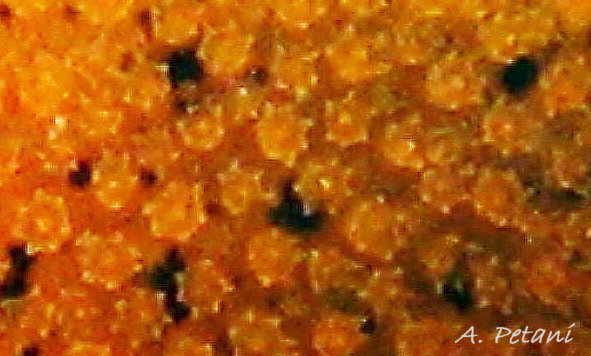
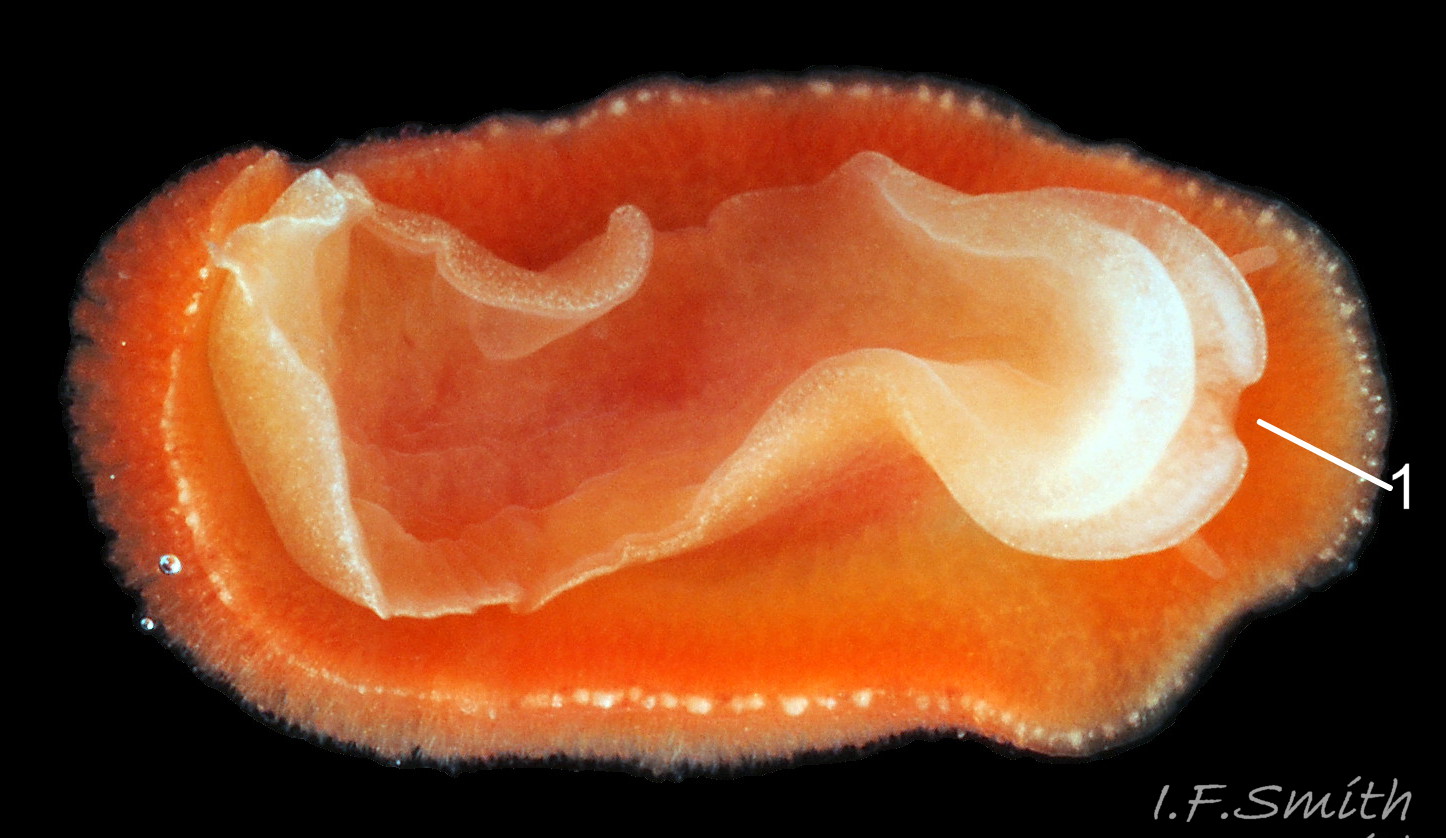
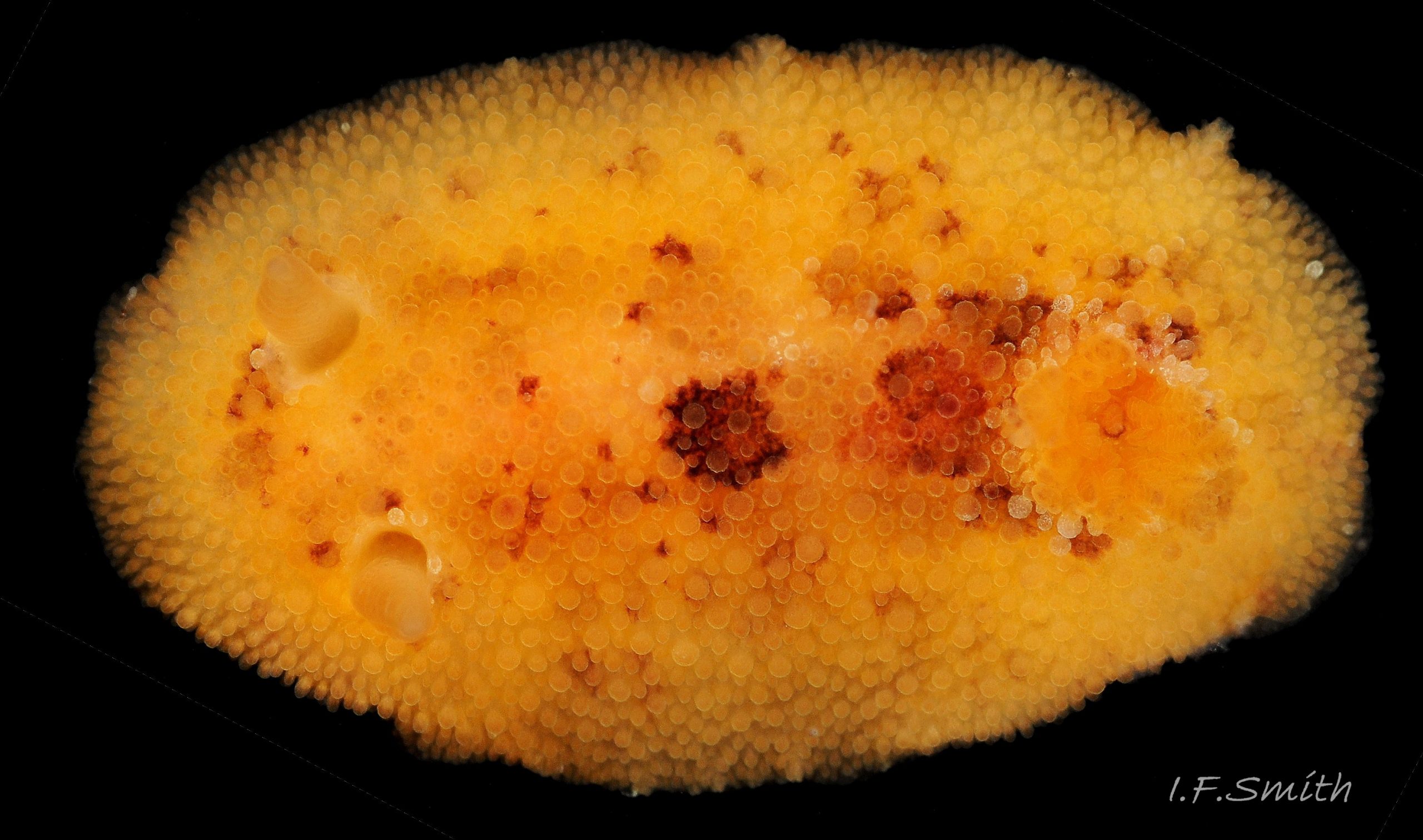
Rostanga rubra grows up to 15 mm long in Britain and 20 mm in the Mediterranean. From above, its outline is an ellipse, narrowest at the posterior 01 Rostanga rubra . Sometimes, when in motion, the sides are almost parallel 02 Rostanga rubra . The ample mantle can cover the whole body. It is covered with densely packed, translucent, spiculate-headed caryophyllidia 03 Rostanga rubra of uniform size and tinted concolorous with the mantle except for the larger, whitish ones around the base of the rhinophores 04 Rostanga rubra . The mantle is scarlet 01 Rostanga rubra , orange 02 Rostanga rubra or orange-yellow with sparse scattered black 03 Rostanga rubra or reddish brown spots 05 Rostanga rubra which are often obscured by the caryophyllidia. There is usually a conspicuous white stripe connecting the rhinophores 06 Rostanga rubra , which, with the white rhinophores, creates a ‘spectacled’ impression. The connecting stripe is sometimes incomplete 02 Rostanga rubra . The perimeter of the mantle is beaded with white caryophyllidia 07 Rostanga rubra . The underside of the mantle is uniformly coloured as the dorsal surface with no markings 08 Rostanga rubra .
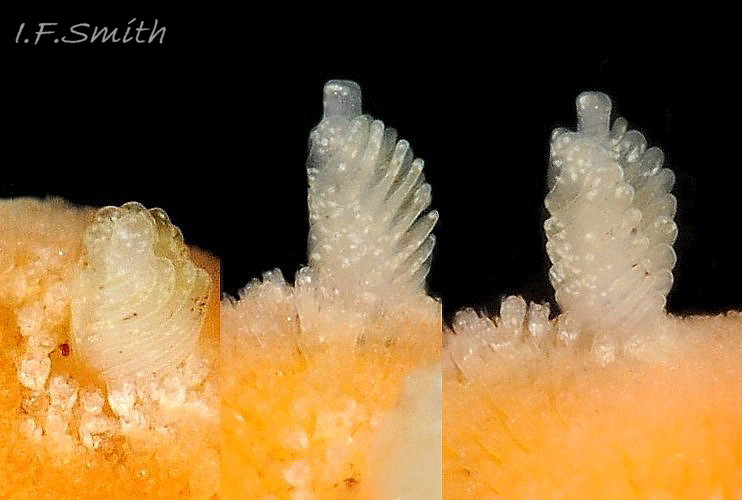
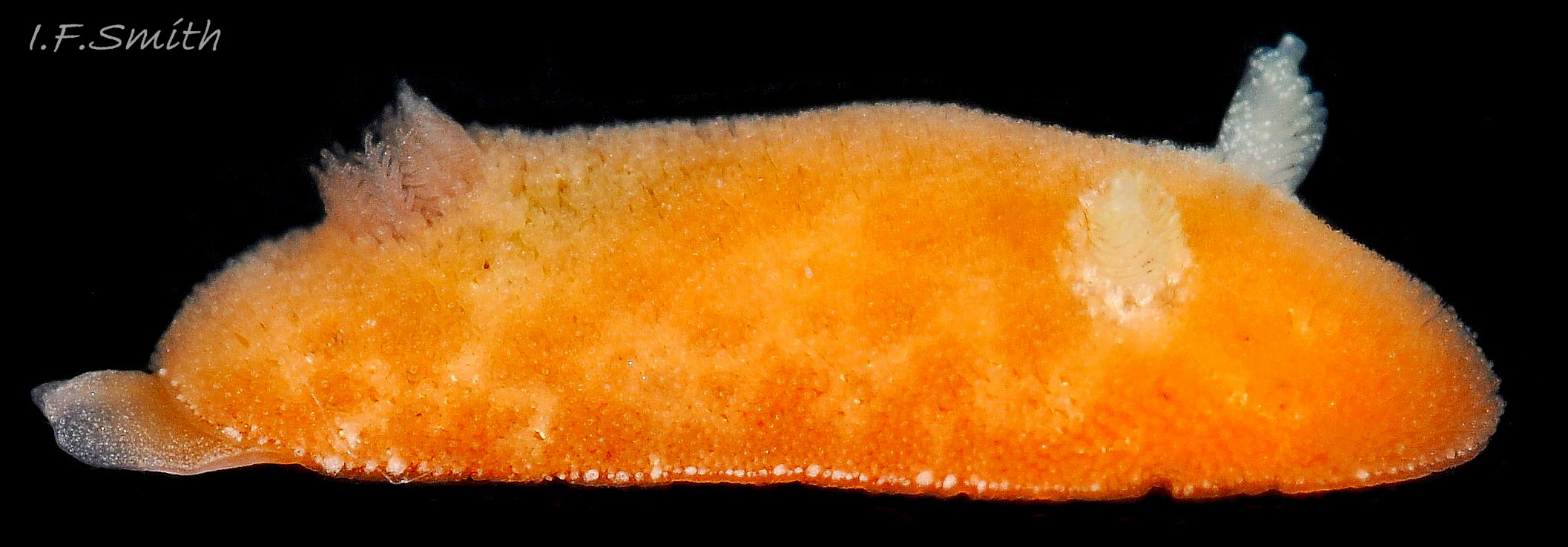
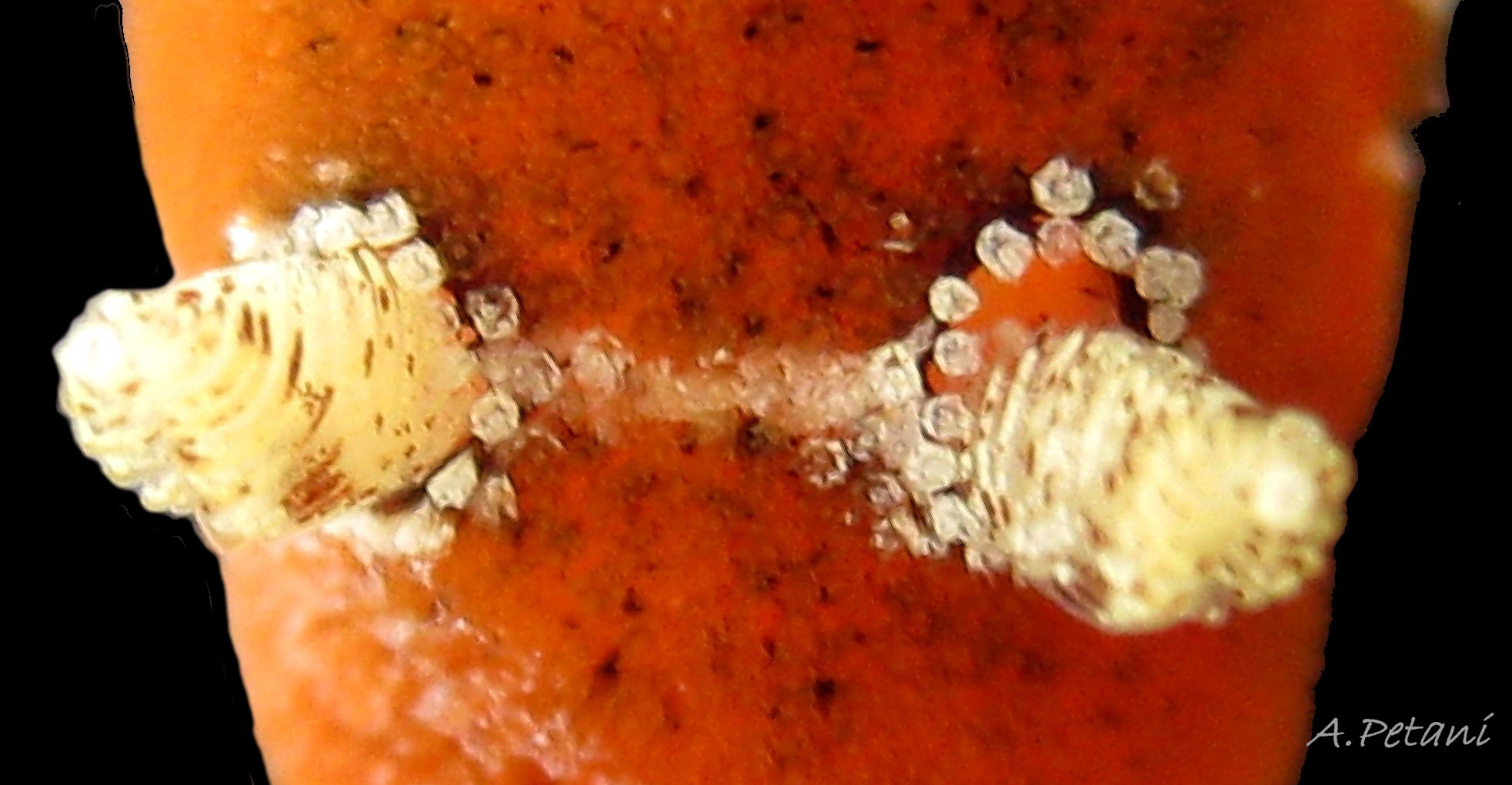
The rhinophores have a slender stem with truncate apex 04 Rostanga rubra . They are translucent white or yellowish white, mottled with opaque white and a few reddish brown spots 06 Rostanga rubra . About nine large lamellae incline up towards the anterior, and are deeply and widely parted down the posterior and, particularly, the anterior.
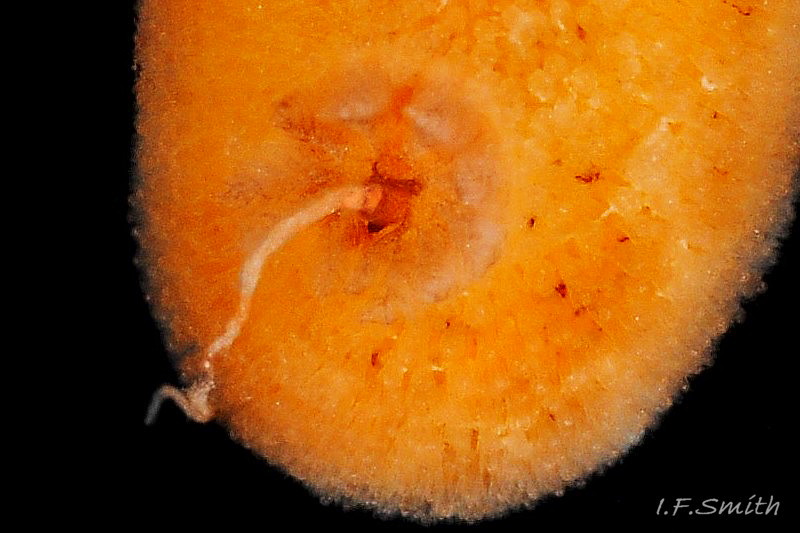
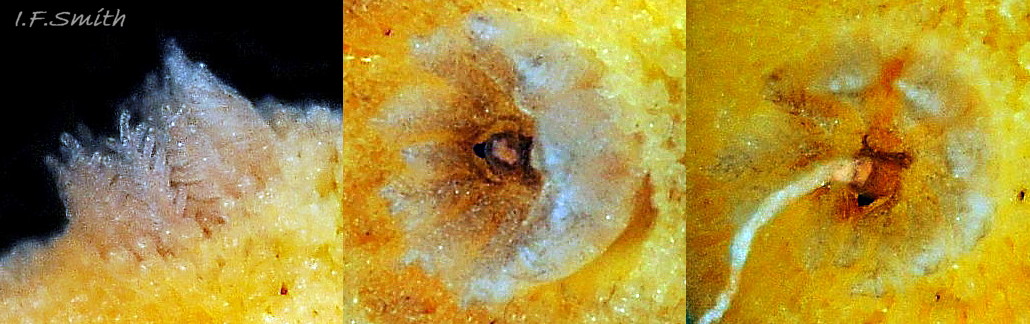
There are up to eleven unipinnate gills on a 10 mm long R. rubra. They rise to form a cylinder 09 Rostanga rubra around the brown, tubular, anal papilla, and are cryptobranchiate 10 Rostanga rubra . They are translucent whitish with a very fine brownish stipple.
Usually, the only visible part of the headis, ventrally, the short oral tentacles 11 Rostanga rubra . The foot protruding at the rear of the body is thin, translucent, tinted a paler shade of the dorsal colour, with a fine, white, opaque stipple 07 Rostanga rubra & 12 Rostanga rubra . The anterior is deeply bilaminate. The upper lamina is deeply notched medially and can extend far forward of the lower lamina 08 Rostanga rubra . The sole is a paler shade of the mantle colour 08 Rostanga rubra & 11 Rostanga rubra .
Key identification features
Rostanga rubra
1) Up to 15mm long (20 mm in the Mediterranean).
2) Mantle bright scarlet, orange or orange-yellow with sparse scattered black 04 Rostanga rubra or reddish-brown spots 05 Rostanga rubra .
3) Conspicuous white stripe connects rhinophores 06 Rostanga rubra , sometimes incomplete 02 Rostanga rubra .
4) Perimeter of mantle beaded with white caryophyllidia 07 Rostanga rubra .
5) Mantle covered with densely packed caryophyllidia 03 Rostanga rubra & 04 Rostanga rubra .
6) Small unipinnate gills usually held erect to form cylinder around brown tubular anal papilla 09 Rostanga rubra .
Similar species
Doris pseudoargus Rapp, 1827. 13 Rostanga rubra & 14 Rostanga rubra.
Only red or orange juveniles less than 16 mm long are likely to be mistaken for R. rubra.
1) Much larger than R. rubra, up to 120 mm long.
2) Often with large blotches of varied bright colours.
3) No white stripe between rhinophores.
4) Perimeter of mantle not beaded with white caryophyllidia.
5) Variously sized blunt rounded tubercles on mantle.
6) Large tripinnate gills tilt backwards and flare outwards.
Habits and ecology
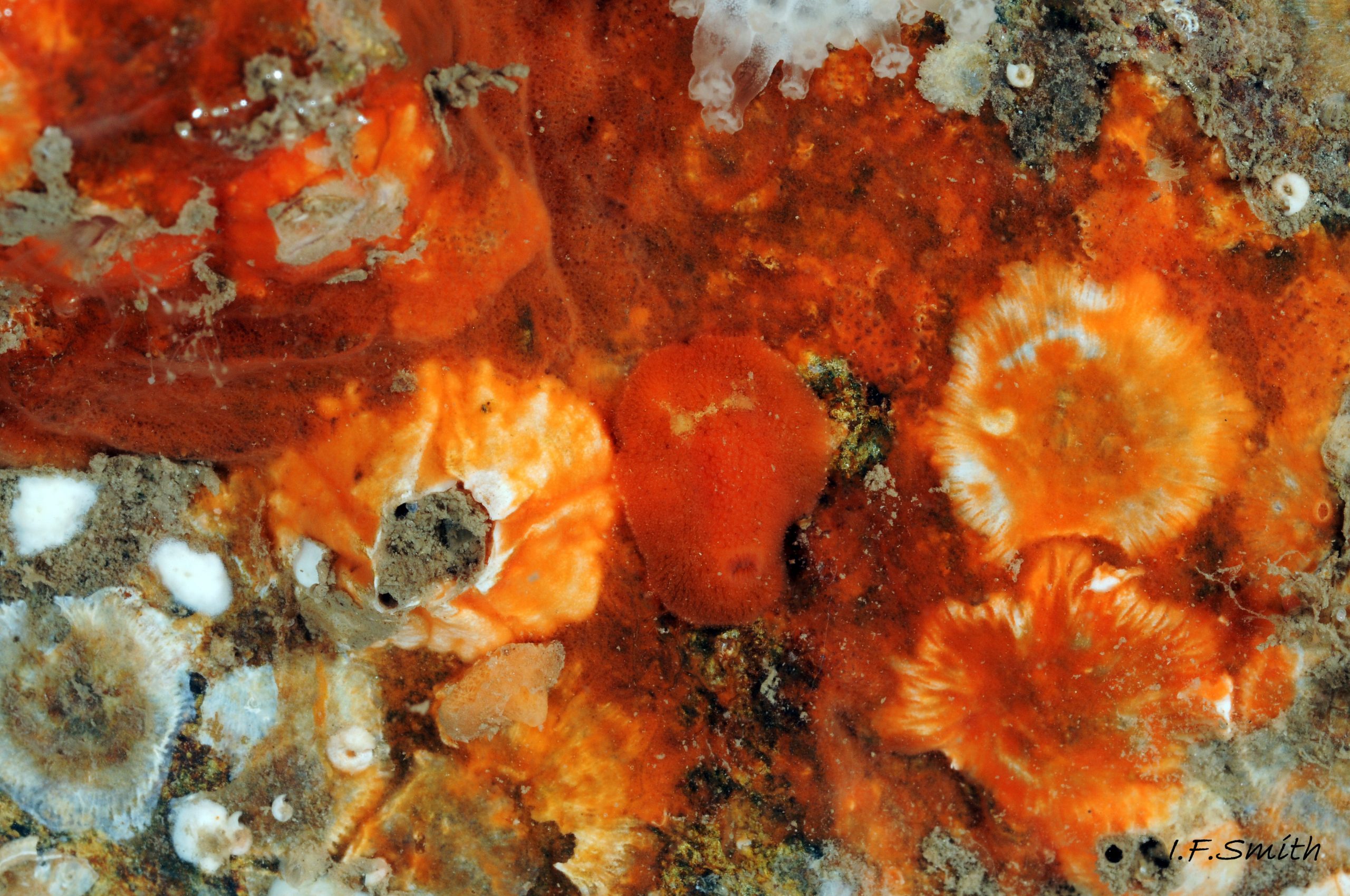
R. rubra lives on rocky substrate on the lower shore, and sublittorally to 60 m. It is well camouflaged on its prey 15 Rostanga rubra of red and orange, encrusting, siliceous sponges such as Microciona atrasanguinea and Ophlitaspongia spp. The tubular brown anal papilla ejects a line of semi-liquid faeces which floats away 05 Rostanga rubra . If it lodges against the gills, individual plumes act like fingers to push it away. It is a simultaneous hermaphrodite, like other nudibranchs. Its spawn has been observed in June and July.
Distribution and status
R. rubra occurs in Mediterranean and Atlantic to Norway; GBIF map www.gbif.org/species/2291966 . There are scattered records round Britain and Ireland; it is scarce or absent from Liverpool Bay, and from Flamborough Head to the Isle of Wight. UK distribution map species.nbnatlas.org/species/NBNSYS0000177747
Acknowledgements
I thank Alen Petani for use of his images from the Adriatic Sea.
References and links
Alder, J. & Hancock, A. 1845-1855. A monograph of the British nudibranchiate mollusca. London, Ray Society. Fam.1 Pl. 7 www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/131598#page/114/mode/1up
Anderson, J. Scottish Nudibranchs www.nudibranch.org/Scottish%20Nudibranchs/
Schmekel, L. & Portmann, A. 1982. Opisthobranchia des Mittelmeeres Nudibranchia und Sacoglossa. Berlin, Springer-Verlag.
Thompson, T.E. & Brown, G.H. 1984. Biology of opisthobranch molluscs 2. London, Ray Society.
Glossary
bilaminate = formed of two laminae (layers).
caryophyllidia = digital tubercles with terminal knob surrounded by coronet of spikes, like a clove (spice), on some dorid sea slugs.
cryptobranchiate = able to retract gills into a single capacious gill cavity.
dorid = a sea slug in the infraorder Doridoidei; with gills and rhinophores on the dorsum; often shaped like half a lemon or grape.
lamellae = small plates on rhinophores, or leaflets of gill.(sing. lamella)
lamina = layer
mantle = (of nudibranchs) sheet of tissue forming part or all of dorsal body-surface.
papilla = (pl. papillae) small protrusion of flesh.
plankton = animals and plants that drift in pelagic zone (main body of water).
rhinophores = chemo-receptor tentacles on top of head of nudibranch.
spicule = small, slender, sharp-pointed feature mainly composed of calcite (CaCO3) and brucite (Mg(OH)2) .
unipinnate = (of gill plume) un-branched simple leaflets along each side of main rib.
veliger = shelled larva of marine gastropod or bivalve mollusc which swims by beating cilia of a velum (bilobed flap).